Blog Details

Why Learning Pronunciations Phonetically gives us a lifelong advantage
As a non-native English speaker it is not only desirable but absolute essential to have good pronunciation skills, to be heard and understood by your peers and colleagues. It becomes especially important if your work includes communicating with native English speakers. Bad pronunciation not only leads to poor communication but can lead to frustration and on some rare occasions even misunderstandings with native English speakers.
The standardized English instruction and education given in Indian schools does not approach the aspect of pronunciation phonetically. Whereas without the use of phonetics and phonology (the sound system or arrangement of a particular language) the study of English spellings and consequently their pronunciation is not only difficult but also incomplete.
The use of phonetics is used by ESL trainers and teachers to teach English as a second language to those who have a different native language. For this purpose trainers use a phonemic chart which contains all the 44 sounds used in standard British English speech (an accent associated with but not exclusive to south-east England). The chart uses symbols from the International Phonemic Alphabet (IPA), which represents different kinds of sounds ranging from long sounds, short sounds, consonant sounds, combined vowel sounds (dipthongs) and single vowel sounds (monopthongs).
For starters every dictionary has a phonetic spelling next to each and every word within its pages but more often than not, Indian students have no idea what they are and how to translate them to sounds. This is where the phonemic chart comes in.
The phonemic chart is a standardized representation of English speech sounds in written form.
The English Phonemic Chart
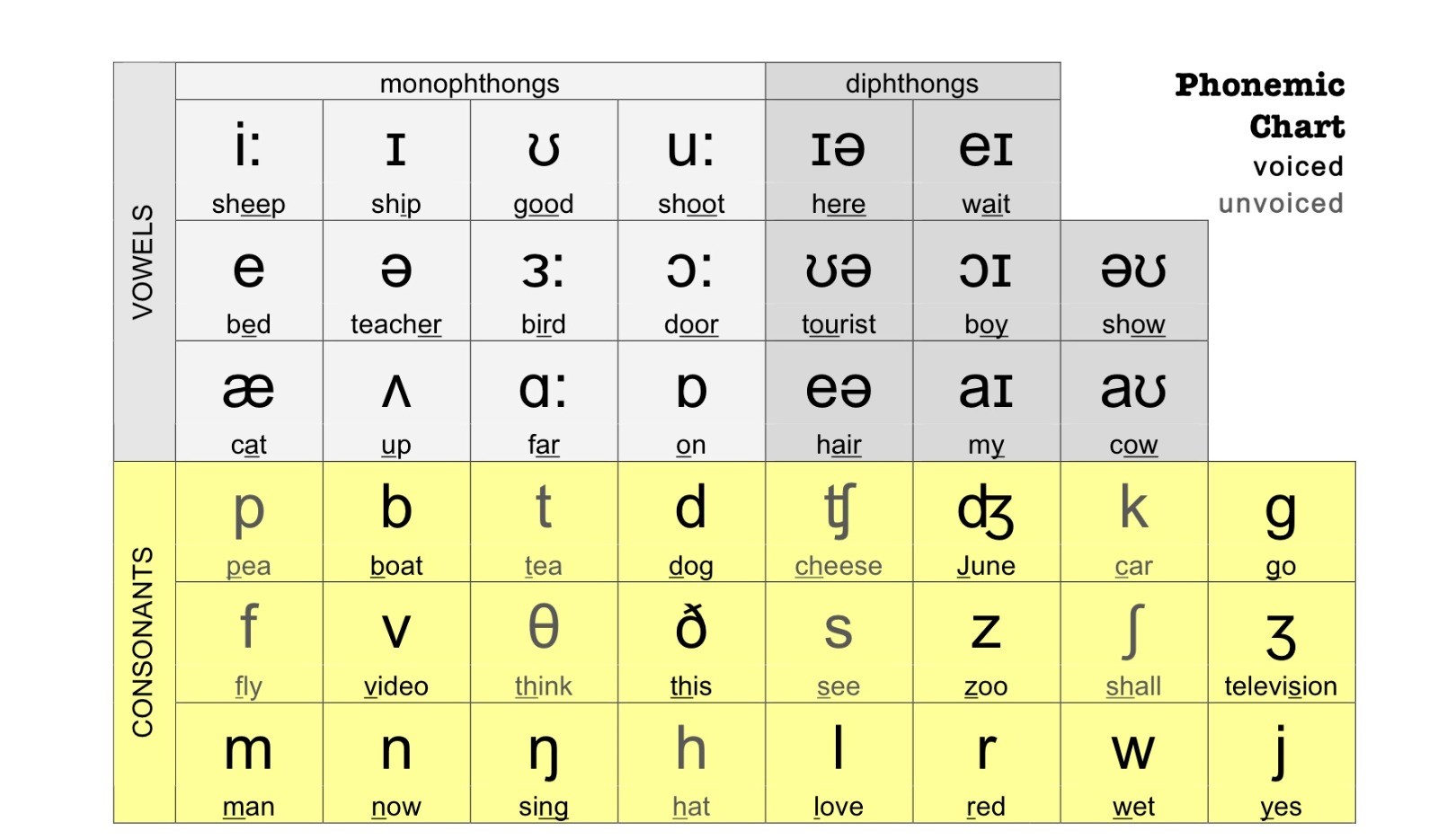
The chart is divided into four sections with:
• Vowel sounds
• Consonant sounds
• Diphthongs
• Monophthongs
This covers all the sounds that can be produced in the English language with word and vowel combinations, with monophthongs being single vowel sounds and dipthongs being combined vowel sounds.
On closer examination, one would observe the highlighted and non-highlighted segments which represent voiced and unvoiced sounds respectively. Simply put voiced sounds are those sounds which require the use and engagement of our vocal chords, while unvoiced sounds are those which do not need the active use of our vocal chords and are produced with the use of tongue, teeth and lips.
Under the monopthongs section, one can observe some symbols with a colon like ‘:’ next to it. This signifies that the symbol corresponds to a long vowel sound which essentially means that it is a long drawn out sound, ex. sheep, leap, door, jar, etc. Short vowel sounds do not have the ‘:’ next to them and are pronounced short and crisp, ex – fat, cat, mat, ship, up, cup, etc.
The main advantage of learning spellings and pronunciations phonetically is that the student gains considerable insight into the knowledge of the English language sound system and becomes an autonomous learner who can pick up a dictionary and pronounce any new word with the help of a phonemic chart.
Since the phonemic chart empowers its user to use translate IPA symbols into sounds, the problematic issue of discerning silent letters disappears altogether. When phonetically translated, any learner of the English language can pronounce any word, no matter how lengthy or complicated it is.
The advantages of learning pronunciation phonetically are follows:
1. It develops comprehension of the English sound system.
2. It makes language learning more focused and imparts a scientific approach to it.
3. It improves the learner’s grasp of vocabulary and language.
4. It develops an understanding of syllable structure.
5. It empowers the independent learner to learn new words and pronounce them correctly.
6. It improves the recognition and translation of IPA symbols.
7. It aids in improving fluency of the learner.
Now that you know how impactful learning language and pronunciation with the help of the phonemic chart can be, will you give it a try?
written by Ms Sampriti Datta, Visiting Faculty at Sanjeevana







